Virtual Studio Technology (VST) is an audio plug-in software interface that integrates software synthesizer and effects in digital audio workstations. VST and similar technologies use digital signal processing to simulate traditional recording studio hardware in software. Thousands of plugins exist, both commercial and freeware, and many audio applications support VST under license from its creator, Steinberg.
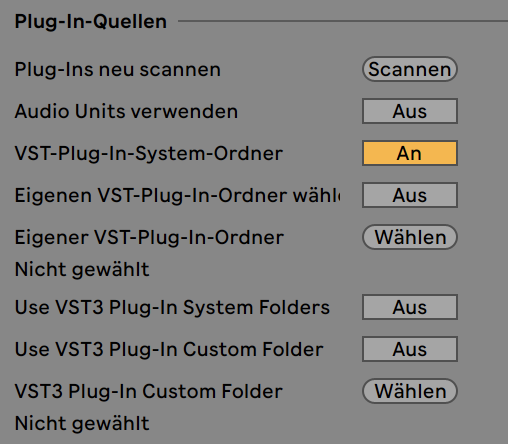
How to install VST or AU plug-ins on Mac. Download the latest installer file from the plug-in manufacturer's website and run it. Most plug-ins will install themselves to the default system folders, others might simply need to be moved to the correct folder. Virtual Studio Technology (VST) is an audio plug-in software interface that integrates software synthesizer and effects in digital audio workstations.VST and similar technologies use digital signal processing to simulate traditional recording studio hardware in software. Thousands of plugins exist, both commercial and freeware, and many audio applications support VST under license from its. 'Use VST Plug-In Custom Folder' if you have installed all or some of the VST plug-ins in a dedicated folder of your own choice, i.e. 'VST Plug-ins'. Click on the Browse button and navigate to this specific folder. Don't set it to a big folder, partition or hard drive as this will crash Live. On a Mac you can also use Audio Units.
Overview[edit]
VST plugins generally run within a digital audio workstation (DAW), to provide additional functionality, though a few standalone plugin hosts exist which support VST. Most VST plugins are either instruments (VSTi) or effects (VSTfx), although other categories exist—for example spectrum analyzers and various meters. VST plugins usually provide a custom graphical user interface that displays controls similar to physical switches and knobs on audio hardware. Some (often older) plugins rely on the host application for their user interface.
VST instruments include software simulation emulations of well-known hardware synthesizers and samplers. These typically emulate the look of the original equipment as well as its sonic characteristics. This lets musicians and recording engineers use virtual versions of devices that otherwise might be difficult and expensive to obtain.
VST instruments receive notes as digital information via MIDI, and output digital audio. Effect plugins receive digital audio and process it through to their outputs. (Some effect plugins also accept MIDI input—for example MIDI sync to modulate the effect in sync with the tempo). MIDI messages can control both instrument and effect plugin parameters. Most host applications can route the audio output from one VST to the audio input of another VST (chaining). For example, output of a VST synthesizer can be sent through a VST reverb effect.
History[edit]
Steinberg released the VST interface specification and SDK in 1996. They released it at the same time as Steinberg Cubase 3.02, which included the first VST format plugins: Espacial (a reverb), Choirus (a chorus effect), Stereo Echo, and Auto-Panner.[2]
Steinberg updated the VST interface specification to version 2.0 in 1999. One addition was the ability for plugins to receive MIDI data. This supported the introduction of Virtual Studio Technology Instrument (VSTi) format plugins. VST Instruments can act as standalone software synthesizers, samplers, or drum machines.[3]
Neon[4] was the first available VST Instrument (included with Cubase VST 3.7). It was a 16-voice, 2-oscillator virtual analog synthesizer.[3]
The VST interface specification was updated to version 2.4 in 2006. Changes included the ability to process audio with 64-bit precision.[5]
VST 3.0 came out in 2008. Changes included:[6]
- Audio Inputs for VST Instruments
- Multiple MIDI inputs/outputs
- Optional SKI (Steinberg Kernel Interface) integration
VST 3.5 came out in February, 2011. Changes included note expression, which provides extensive articulation information in individual note events in a polyphonic arrangement. According to Steinberg, this supports performance flexibility and a more natural playing feel.[7]
In October 2011, Celemony Software and PreSonus released Audio Random Access (ARA), an extension for audio plug-in interfaces, such as VST, allowing greater integration between audio plug-ins and DAW software.[8]
In September, 2013, Steinberg discontinued maintenance of the VST 2 SDK. In December, Steinberg stopped distributing the SDK.[9] The higher versions are continued.
VST 3.6.7 came out in March, 2017. It includes a preview version of VST3 for Linux platform, the VST3 part of the SDK gets a dual license: 'Proprietary Steinberg VST3' or the 'Open-source GPLv3'.
As VSTi virtual instrument technology was under development at Steinberg, a platform for virtual instruments using DirectX engine technology was being developed by Cakewalk, famous for its Sonar DAW. However, the format did not gain much acceptance beyond instruments bundled with SONAR. Currently, almost all virtual instruments on the market use Steinberg's VSTi format.[citation needed]
VST plugins[edit]
Free Ableton Vst Plug-ins
There are three types of VST plugins:
- VST instruments generate audio. They are generally either Virtual Synthesizers or Virtual samplers. Many recreate the look and sound of famous hardware synthesizers. Better known VST instruments include Discovery, Nexus, Sylenth1, Massive, Omnisphere, FM8, Absynth, Reaktor, Gladiator, Serum and Vanguard.
- VST effects process rather than generate audio—and perform the same functions as hardware audio processors such as reverbs and phasers. Other monitoring effects provide visual feedback of the input signal without processing the audio. Most hosts allow multiple effects to be chained. Audio monitoring devices such as spectrum analyzers and meters represent audio characteristics (frequency distribution, amplitude, etc.) visually.
- VST MIDI effects process MIDI messages (for example, transpose or arpeggiate) and route the MIDI data to other VST instruments or to hardware devices.
VST hosts[edit]
A VST host is a software application or hardware device that VST plugins run under. The host application presents the plugin UIs and routes digital audio and MIDI to and from the plugins.
Software[edit]
Many VST hosts are available. Not all of these support VST 3 plugins.
- Acon Digital Acoustica
- Acoustica Mixcraft (VST3)
- Ardour (open source)
- Audacity (free and open source, VST support works on Windows, Mac OS X and Linux[10])
- Digital Performer (version 8 or higher)
- Maschine[11]
- Reason (version 9.5 or higher)[12]
- Psycle (open source)
- vMix (VST3 Only)
Stand-alone dedicated hosts provide a host environment for VST plugins rather than use the plugins to extend their own capabilities. These are usually optimized for live performance use, with features like fast song configuration switching.
VST plugins can be hosted in incompatible environments using a translation layer, or shim. For example, FL Studio only supports its own internal plugin architecture, but an available native 'wrapper' loads VST plugins, among others. FXpansion offers a VST-to-RTAS (Real Time AudioSuite) wrapper that lets VST plugins run in Pro Tools, and a VST-to-Audio Units wrapper lets VST plugins run in Logic Pro.
Hardware[edit]
Hardware VST hosts can load special versions of VST plugins. These units are portable and usable without a computer, though some of them require a computer for editing. Other hardware options include PCI/PCIe cards designed for audio processing, which take over audio processing from the computer's CPU and free up RAM.
Some hardware hosts accept VSTs and VSTis, and either run Windows-compatible music applications like Cubase, Live, Pro Tools, Logic etc., or run their own DAW. Other are VST Hosts only, and require a separate DAW application. Origin from Arturia is a hardware DSP system that houses several VST software synthesizers in one machine, like Jupiter 50/80 from Roland. Using appropriate software, audio data can also be sent over a network, so the main host runs on one computer, and VST plugins on peripheral machines.
VST plugin standard[edit]
The VST plugin standard is the audio plugin standard created by Steinberg to allow any third party developers to create VST plugins for use within VST host applications. VST requires separate installations for Windows, Mac OS X and Linux. The majority of VST plugins are available for Windows only due to Apple's competing proprietary Audio Unit technology being used on OS X (Audio Units is a core part of the OS X operating system). The short history of commercial environments for Linux means few developers have targeted this platform.
Presets[edit]
VST plugins often have many controls, and therefore need a method of managing presets (sets of control settings).
Steinberg Cubase VST introduced two file formats for storing presets: an FXP file stores a single preset, while an FXB file stores a whole bank of presets. These formats have since been adopted by many other VST hosts, although Cubase itself switched to a new system of preset management with Cubase 4.0.
Many VST plugins have their own method of loading and saving presets, which do not necessarily use the standard FXP/FXB formats.
Competing technologies[edit]
- Apple's Audio Units
- Avid's Avid Audio eXtension
- Digidesign's Real Time AudioSuite
- Digidesign's TDM
- LADSPA, DSSI for Linux
- LV2, a cross-platform, open source, liberally licensed audio plugin standard
- Microsoft's DirectX plugin
- Mark of the Unicorn's Motu Audio System
- JACK Audio Connection Kit, an open source sound server allowing flexible audio routing between apps
- Propellerhead's Rack Extensions
Programming languages[edit]
Steinberg's VST SDK is a set of C++ classes based around an underlying C API. The SDK can be downloaded from their website.
There are several ports available, such as a Delphi version by Frederic Vanmol,[13] a Java version from the jVSTwRapper project at Sourceforge,[14] and two .NET versions – Noise[15] and VST.NET;[16] this open source project also includes a framework that makes creating VST plugins easier and result in more structured code. VST.NET also provides support for writing managed host applications with a managed class that allows loading an unmanaged Plugin. A notable language supporting VST is FAUST, considering that it is especially made for making signal processing plugins, often producing code faster than hand-written C++.
In addition, Steinberg have developed the VST GUI, which is another set of C++ classes, which can be used to build a graphical interface. There are classes for buttons, sliders and displays etc. Note that these are low level C++ classes and the look and feel still have to be created by the plugin manufacturer. VST GUI is part of the VST SDK and is also available as sourceforge project in http://sourceforge.net/projects/vstgui .
Many commercial and open-source VSTs are written using the Juce C++ framework instead of direct calls to the VST SDK, because this allows multi-format (VST, Audio Units and Real Time AudioSuite) binaries to be built from a single codebase.
See also[edit]
- LADSPA and LV2, similar open source standards.
- SynthEdit, a VST/VSTi editor.
References[edit]
- ^'Our Technologies'. www.steinberg.net.
- ^Steinberg Cubase 3 (article), Sound on sound, Jul 1996.
- ^ abCubase 3.7 (article), Sound on sound, Sep 1999
- ^KVR audio.
- ^Steinberg.
- ^News, KVR audio.
- ^VST 3.5 a milestone in VST development (News), Steinberg, 2011-02-10.
- ^'Celemony introduces ARA Audio Random Access - Extension for Plug-in Interfaces'. KVR Audio. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
- ^SDK for VST 2 software interface discontinued (News), Steinberg, 2013-12-09
- ^VST plug-ins
- ^http://www.native-instruments.com/en/products/maschine/production-systems/maschine/
- ^https://www.propellerheads.se/reason-95
- ^VST, Axi world.
- ^jVSTwRapper, Source forge.
- ^Noise, Google code.
- ^VST.Net, Codeplex.
Although we have all the tools we need to produce extremely clean and precise music without any unwanted artefacts there’s something about the imperfections of analog recording equipment that triggers certain emotions in us.
So if you want to produce lofi music it’s important to pick the right sounds and samples from the start. You could, for example, sample old vinyl records or buy an old drum machine. It would however be easier to just get your hands on a decent LoFi House or Hip Hop sample pack.
Once you have a selection of cool sounds & samples you can further refine your music to sound like it was recorded a few decades ago. Luckily there are plenty of cool lofi plugins available so you don’t have to actually own an old tape machine. Here are some of the best options:
Free LoFi Plugins
I want to start this list with a bunch of free lofi VSTs, because I know that a lot of producers are one a budget, especially when they’re still going to school (or music is their only income lol). That said, you don’t always have to spend money to get some quality software. The freeware in this list can easily compete with some of the paid stuff I’ll mention later on.
BVKER LoFi Rack
The “LoFi Rack” is a free Ableton Rack based on Live’s stock plugins. It comes with 8 macros allowing you to decrease the band width, add vinyl crackles, detune and distort the source sound. Unfortunately it’s only available for Ableton Live users, so if you’re using another DAW you have to pick some of the other options in this list. If you’re using Ableton however, hop on my newsletter and I’ll send you a free download link.

iZotope Vinyl
As the name suggests, iZotope’s “Vinyl” is a plugin emulating the characteristic imperfections of vinyl records. Since the freeware only comes with a handful of parameters it’s easy to use and setting it up won’t take much time. What I love the most is that you can adjust the year of your “recording”. A must have for every lofi producer if you ask me.
Spitfire Audio Labs
Labs is a free software instrument made by the London based sound design company Spitfire Audio. There are several extensions available, including pianos, brass, choirs and synths. Most of these instruments are rather unique and therefore a nice addition to the basic instruments libraries you probably already own. The cool part about Labs is that it comes with only a handful of parameters so you won’t spend 10 years trying to get everything perfect. The sound either fits your production or not.
Tritik Krush
Tritik’s Krush is an effect plugin with 3 different distortion types. A bitcrusher , a downsampler and an analog drive knob. It further comes with 2 filters and an LFO that can be used to modulate every parameter. It’s available for both Windows and Mac in VST, AU and AAX format so really everyone can get their hands on this.
HY-Lofi2
This one is a free bit quantizer, waveshaper & filter plugin made by Tadashi Suginomori from HY-Plugins. It’s meant to process “audio to give it a low fidelity sound”. Just like Krush it combines different distortion modes with high and low-pass filters. More precisely it has one drive knob and a quantizer, which can run in different modes and qualities.
Legowelt Ableton Racks
Legowelt is a dutch producer known for releasing samples from analog hardware units, but you’ll also find some Ableton Racks on his website, including the Smackos Tape Station, the Smackos Lemuria Vintage Sampler Simulator, the Smackos 808 Simulator and the Smackos Amiga 909.
Sound-Base Audio Retro Boy
The Retro Boy is a Windows only VST synth. It comes with one oscillator, 7 waveforms and controls for ADSR, vibrato and decimation, which makes it perfect for Chiptune or 8-bit music. Since there isn’t much processing going on, the synth is quite CPU-friendly.
Best LoFi Plugins
Although you can definitely do some cool stuff with the freeware I mentioned so far there are some paid options no lofi producer should miss out on. A lot of them do more or less the same thing so in the end it’s up to personal preference (and budget), which ones you should get. Luckily most of these plugins aren’t that expensive compared to some of the stuff by other brands.
XLN Audio RC-20 Retro Color
Probably the most hyped plugin of this list is the R-c20 Retro Color by XLN Audio. It combines 6 different effect units, including noise, wobble, distort, digital, space and magnetic. Combining these options basically allows you to recreate any lofi characteristic you could possibly think of. If I could only pick one plugin of this list I’d probably go for this one, since it comes with the most features.
Baby Audio Super VHS
Considering that Baby Audio is a rather new plugin company, their products already gained quite much attention. Super VHS again combines multiple effects, including a distortion unit, a retro sounding reverb and detune knob labeled “drift”. All knobs sound surprisingly good and I really dig the design.
D16 Group Decimort 2
Decimort 2 is a bitcrusher on steroids. It offers two optional anti-alias filters, adjustable jitter, two quantization methods and controllable dithering. If you’re looking for a cool bitcrusher, this is definitely the one you should get your hands on. With less than 50 bucks it’s also pretty affordable.
AudioThing Vinyl Strip
The Vinyl Strip is just like RC-20 a multi-effect plugin consisting of 6 different modules: Distortion, Compressor, Bit Crusher, Tilt EQ, Vintage Reverb, and something they call Vinylizer. In contrast to most plugins mentioned in this list, you can change the signal flow simply via drag-n-drop. On their website is stated that you can activate your license without an internet connection, which is pretty cool if you still live in a cave 😉
Devious Machines Texture
Texture is a plugin I just recently found out about watching Virtual Riot’s production workshop he did for Cymatics. It allows you to add noise to any kind of source sound. The cool part is that unlike similar effects you can even load your own noise samples and can adjust the exact frequency range, amount, ADSR and stuff like that.
Cableguys ShaperBox
When it comes to beat making, there’s one plugin every FL Studio user slaps on their melodies: Gross Beat (you’ll find plenty of memes about this). The problem is that it can’t be used in other DAWs (at least on Mac). This is where the Cableguys come into play. Their ShaperBox combines different effects that can all be modulated. The Time one is especially interesting for lofi producers, because it allows you to play back your melodies in halftime, add cool pitching effects and mix everything in with the dry signal.
Initial Audio Analog Pro
Analog Pro is once again a plugin meant to bring your digital audio tracks to live by simulating analog hardware. It comes with a variety of adjustable controls, including Noise Level, Noise Type, Impulse Type, Impulse Mix, Emphasis, Stereo, Lowcut, Highcut, Wow, Flutter and Amount. While I’m writing this the plugin is on sale for €26.10 (which is 64% off) so feel free to check out if this offer is still available.
Aberrant DSP SketchCassette
SketchCassette is a VST inspired by 4-track cassette recorders. It comes with most features the other plugins in this list have. Since it’s however available for only $20 it’s particularly interesting for producers on a tight budget.
Goodhertz Wow Control
Wow Control focuses on the weird and random modulations of analog playback devices. According to their website Goodhertz has carefully studied the essence of three different tape machines to make sure their plugin is the most comprehensive tape model they ever heard. I haven’t tried it out to be honest, but there are some videos about it on YouTube so feel free to check them out if you’d like to learn more about it.
PSPaudioware VintageWarmer2
The PSP Vintage Warmer is a tool simulating the saturation of analog compression / limiting. It comes with classic compression controls, such as knee or release time, and since it can run in multiband mode you can further control the individual bands a bit. In contrast to most usual compressors it comes with a big drive knob. Since it also comes with a mix knob you can drive the compression / saturation quite hard and mix it in just a bit to make your drums or vocals or whatever a bit fatter.
Wavesfactory Cassette
According to Wavesfactory’s website “Cassette is an audio plugin that imparts the unique character and sonic imprint of an often maligned recording medium”. You can also get your hands on their free Cassette Transport plugin, which “simulates the sound of tape speeding up and slowing down”. Or with other words: it’s a pretty cool tape stop plugin.
Psychic Modulation EchoMelt
Audio Plugins For Mac
Echomelt is “designed for adding character, texture and warmth to your sounds”. It doesn’t look that stunning, but it comes with an echo and chorus unit, which sets it apart from the other options in this list.
Aphex Vintage Exciter
The Aphex Vintage Aural Exciter by Waves is modeled on a tube-powered hardware unit. It allows you to increase high frequencies without raising the level too much.
Conclusion
How To Install Vst Mac
As you can see, there are plenty of lofi plugins available that make your productions sound like they were recorded with a toaster (or something like that). The free offers, especially Vinyl and Labs are no brainers, since .. well, they’re free, so make sure to download them straight away if you haven’t done so yet 😉